Bird Flu in 2024: Understanding the Risks and Challenges
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, continues to be a critical topic of discussion in 2024. As global health experts work tirelessly to manage emerging strains, individuals need to stay informed about the potential risks, transmission, and prevention strategies associated with bird flu. This blog delves into the current state of bird flu, highlighting its impact on public health, agriculture, and global economies.
What is Bird Flu?
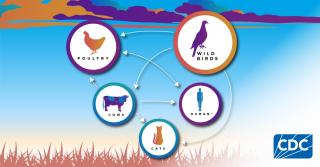
Bird flu refers to a group of influenza viruses primarily found in birds. These viruses, particularly the H5N1 and H7N9 strains, have caused significant outbreaks among poultry and wild bird populations. While bird flu is predominantly an avian disease, certain strains have crossed the species barrier, infecting humans and raising global health concerns. The term "bird flu" has become synonymous with zoonotic risk, making it a focal point for epidemiologists in 2024.
Bird Flu in 2024: A Global Snapshot
In 2024, bird flu remains a pressing issue due to its ability to mutate and adapt. Reports from the World Health Organisation (WHO) indicate a rise in avian influenza outbreaks in Asia, Europe, and Africa. The H5N1 strain, in particular, has been responsible for substantial poultry losses and sporadic human infections. The bird flu situation underscores the interconnectedness of animal and human health, emphasizing the importance of the One Health approach.
How Does Bird Flu Spread?
Bird flu spreads primarily through direct contact with infected birds, their droppings, or contaminated environments. Live bird markets and poultry farms are common hotspots for transmission. In rare cases, human-to-human transmission of bird flu has been documented, though it remains inefficient. The highly pathogenic nature of certain bird flu strains necessitates stringent biosecurity measures to curtail outbreaks.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans
Infected individuals may experience symptoms ranging from mild respiratory distress to severe complications such as pneumonia. Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
In severe cases, bird flu can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or multi-organ failure. Early detection and treatment are critical for improving outcomes in bird flu patients.
The Economic Impact of Bird Flu
The bird flu outbreaks of 2024 have had far-reaching economic consequences. Poultry farmers face devastating losses as large-scale culling of birds becomes necessary to control the spread. The poultry industry, a vital source of protein and livelihood for millions, is grappling with rising costs and reduced exports. Additionally, bird flu outbreaks can lead to reduced consumer confidence, affecting food supply chains and market stability.
The Role of Vaccines in Combating Bird Flu
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in the fight against bird flu. In 2024, advancements in vaccine technology have led to the development of more effective avian influenza vaccines for both poultry and humans. However, challenges such as production scalability and strain-specific effectiveness persist. Efforts to expand vaccine coverage are critical in mitigating the impact of bird flu.
Bird Flu and Public Health Preparedness
Public health systems worldwide have prioritized bird flu preparedness, focusing on early detection, rapid response, and containment. Enhanced surveillance systems, genetic sequencing of viruses, and international collaboration are crucial components of bird flu management in 2024. Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating communities about bird flu prevention and reporting.
Preventing Bird Flu: Tips for Individuals
To reduce the risk of bird flu, individuals should adhere to the following precautions:
- Avoid contact with wild birds: Refrain from handling sick or dead birds.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash hands frequently and maintain cleanliness in areas where poultry is handled.
- Cook poultry thoroughly: Ensure that chicken and eggs are cooked to an internal temperature of at least 74°C (165°F).
- Stay informed: Keep updated on bird flu outbreaks and follow guidelines issued by health authorities.
The Link Between Bird Flu and Wildlife Conservation
Bird flu has significant implications for wildlife conservation. Migratory birds, often carriers of avian influenza, are integral to ecosystems. Balancing bird flu management with conservation efforts is a delicate task. Strategies such as habitat protection and surveillance of wild bird populations help mitigate bird flu risks while preserving biodiversity.
Bird Flu and Climate Change
Climate change exacerbates the bird flu threat by altering migratory patterns and expanding the range of avian hosts. Warmer temperatures and changing habitats create conditions conducive to the spread of bird flu. Addressing the link between climate change and bird flu is crucial for long-term prevention strategies.
Research and Innovation in Bird Flu Control
In 2024, researchers are leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and genome editing to combat bird flu. AI-driven predictive models help identify potential outbreak hotspots, while CRISPR technology enables precise genetic modifications in viruses. These innovations pave the way for more effective bird flu management and control.
International Cooperation in Tackling Bird Flu
Bird flu knows no borders, making international collaboration essential. Organizations such as the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) work closely with governments to monitor and respond to bird flu outbreaks. Sharing data, resources, and expertise is key to reducing the global burden of bird flu.
The Future of Bird Flu: Challenges and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the fight against bird flu requires sustained efforts and investments. Challenges such as vaccine accessibility, public compliance, and environmental factors must be addressed. At the same time, advancements in science and technology offer hope for more effective bird flu prevention and control measures.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against Bird Flu
Bird flu remains a significant public health and economic challenge in 2024. By staying informed and proactive, individuals, communities, and governments can collectively reduce the impact of bird flu. As we navigate the complexities of this zoonotic disease, continued vigilance, and innovation are essential to safeguarding global health from the ever-evolving threat of bird flu.


.png)


.jfif)

.jpg)




0 Comments